Uniform Spatial Partitions (Grids)
Preprocess – Build Acceleration Grid
- Find bounding box
- Create grid
- Store each object
in overlapping cells
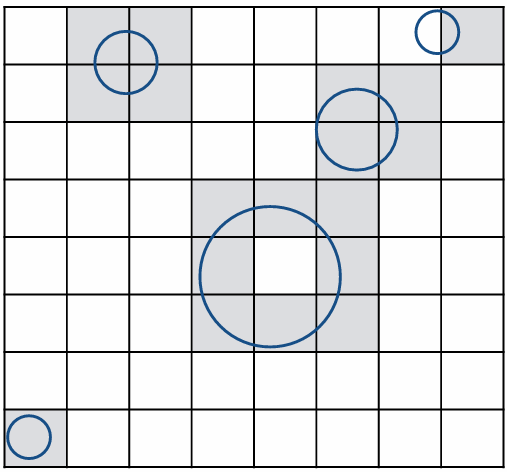
Grid Resolution?
One cell
• No speedup
Too many cells
• Inefficiency due to extraneous grid traversal
需要平衡格子数量
Grids work well on large collections of objects that are distributed evenly in size and space
在分布均匀的物体上,格子方法效果不错
Spatial Partitions
空间划分
Spatial Partitioning Examples
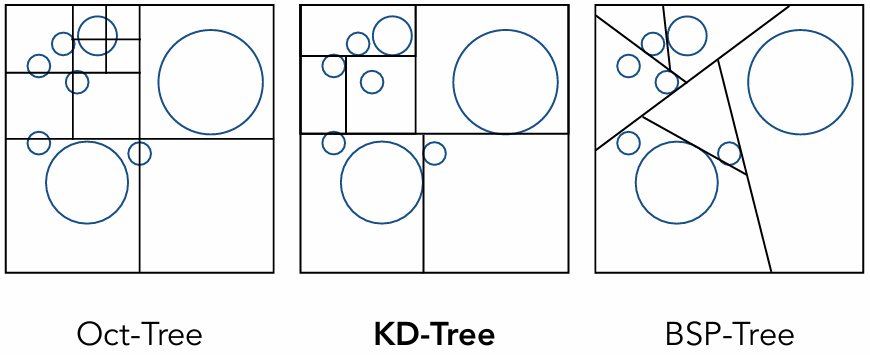
Oct-tree:对空间不断八分 (2维是4分)
KD-tree:不断沿着轴方向二分
BSP-tree:不是横平竖直来划分,斜着
Data Structure for KD-Trees
Internal nodes store
• split axis: x-, y-, or z-axis
• split position: coordinate of split plane along axis
• children: pointers to child nodes
• No objects are stored in internal nodes
中间节点不存储物体,只存在叶子节点(不再划分的节点)上
Leaf nodes store
• list of objects
存在的问题:
1 物体可能存在多个格子里
2 难以判断三角形是否在一个格子里(如格子插入三角形的情况,无法只用顶点来判断)
Object Partitions & Bounding Volume Hierarchy (BVH)
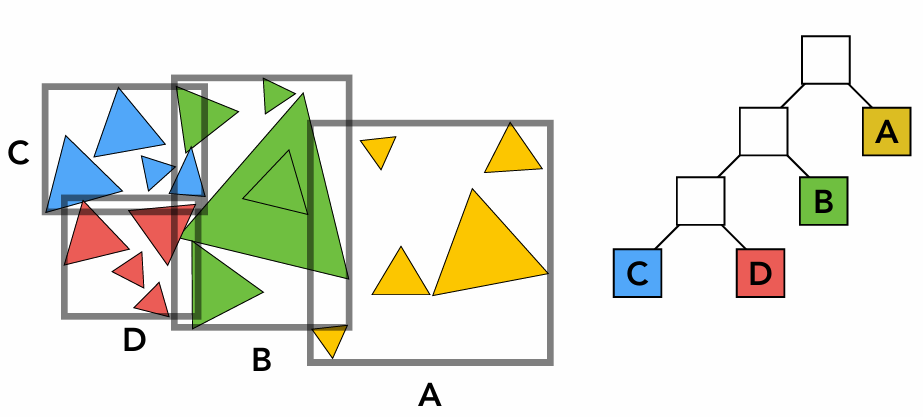
不断划分物体
• Find bounding box
• Recursively split set of objects in two subsets
• Recompute the bounding box of the subsets
• Stop when necessary (例如三角形足够少)
• Store objects in each leaf node
Building BVHs
How to subdivide a node? 小技巧
• Choose a dimension to split
• Heuristic #1: Always choose the longest axis in node
• Heuristic #2: Split node at location of median object 让分割后两部分物体数量差不多 (可以使用快速划分算法)O(n)
Termination criteria?
• Heuristic: stop when node contains few elements
Data Structure for BVHs
Internal nodes store
• Bounding box
• Children: pointers to child nodes
Leaf nodes store
• Bounding box
• List of objects
Nodes represent subset of primitives in scene
• All objects in subtree
Spatial vs Object Partitions
Spatial partition (e.g.KD-tree)
• Partition space into
non-overlapping regions
• An object can be contained in multiple regions
Object partition (e.g. BVH)
• Partition set of objects into disjoint subsets
• Bounding boxes for each set may overlap in space
Radiometry
Measurement system and units for illumination
Accurately measure the spatial properties of light
-New terms: Radiant flux, intensity, irradiance, radiance
Perform lighting calculations in a physically correct manner
Radiometry — Motivation
Observation
• In assignment 3, we implement the Blinn-Phong model
• Light intensity I is 10, for example
• But 10 what?
Do you think Whitted style ray tracing gives you CORRECT results?
All the answers can be found in radiometry
• Also the basics of “Path Tracing”
Radiant Energy and Flux (Power)
Definition: Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation.
It is measured in units of joules, and denoted by the symbol:
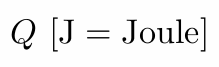
Definition: Radiant flux (power) is the energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit time.
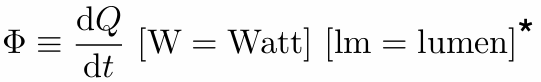
Important Light Measurements of Interest
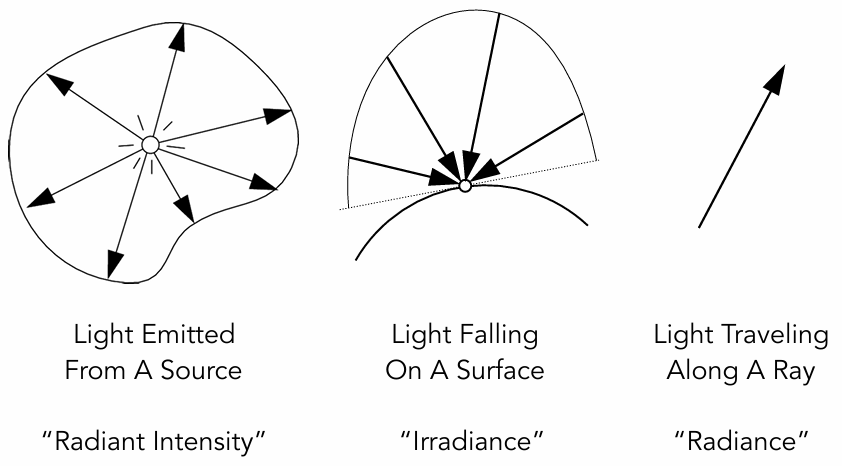
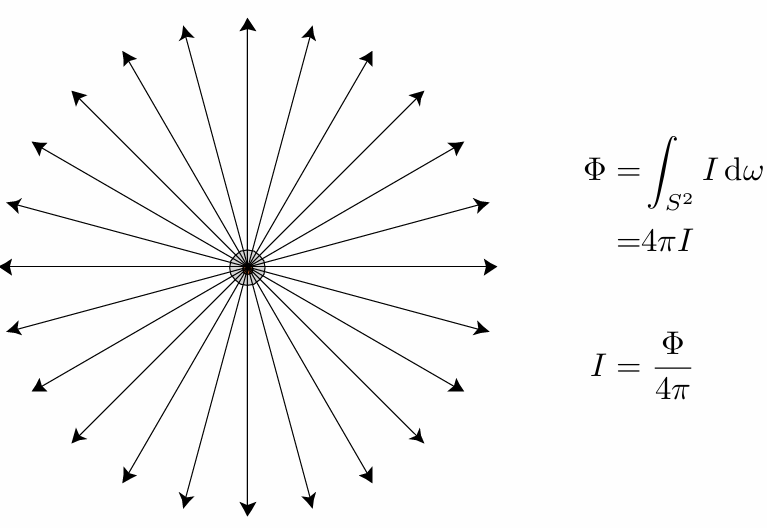
Radiant Intensity
Definition: The radiant (luminous) intensity is the power per unit solid angle (立体角) emitted by a point light source.
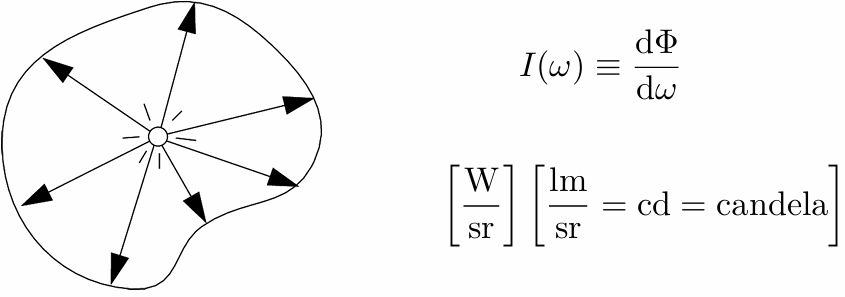
The candela is one of the seven SI base units.
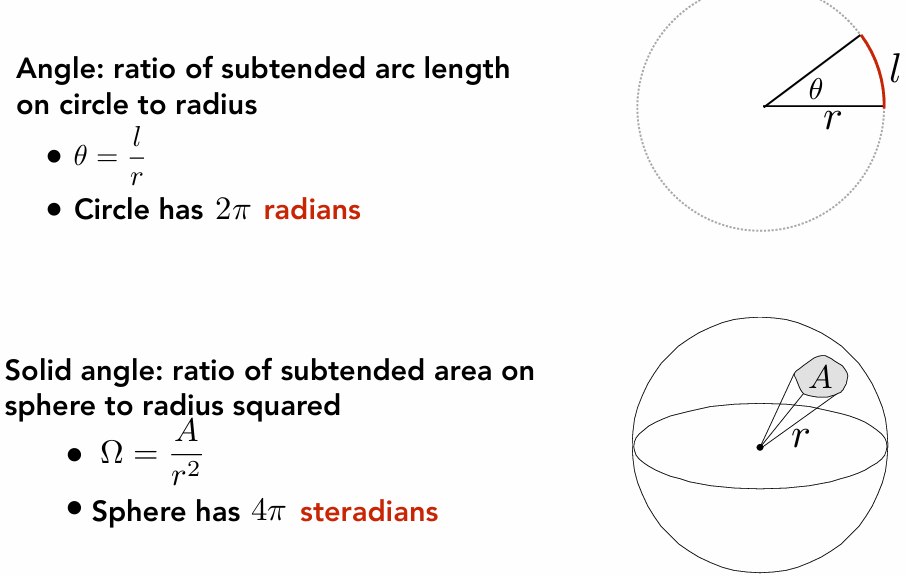
Angles and Solid Angles
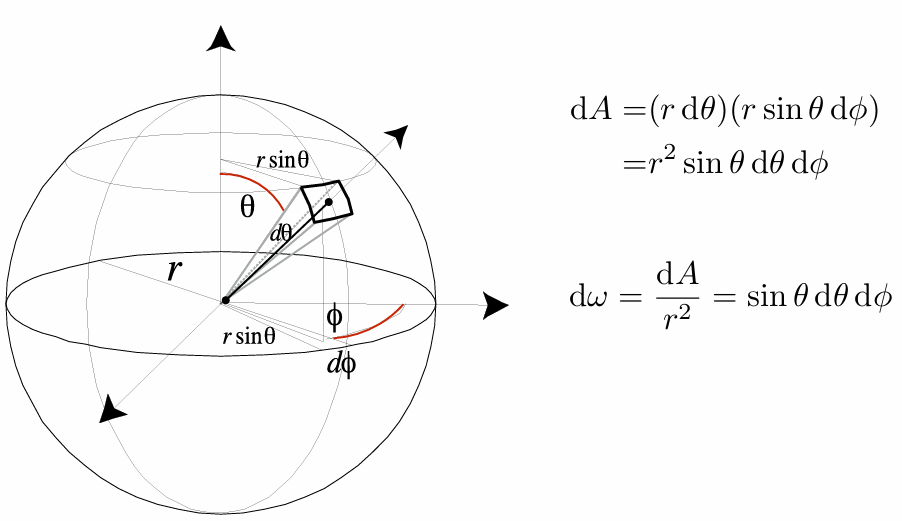
Differential Solid Angles 单位/微分立体角
Isotropic Point Source 各向同性光源