Explicit Representations in Computer Graphics
Many Explicit Representations in Graphics
triangle meshes
Bezier surfaces
subdivision surfaces
NURBS
point clouds
…
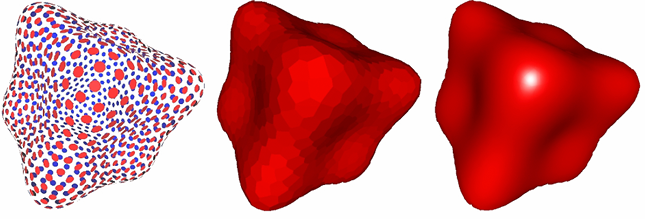
Point Cloud (Explicit)
Easiest representation: list of points (x,y,z)
Easily represent any kind of geometry
Useful for LARGE datasets (>>1 point/pixel)
Often converted into polygon mesh
Difficult to draw in undersampled regions
Polygon Mesh (Explicit)
Store vertices & polygons (often triangles or quads)
Easier to do processing / simulation, adaptive sampling
More complicated data structures
Perhaps most common representation in graphics
The Wavefront Object File (.obj) Format
Commonly used in Graphics research
Just a text file that specifies vertices, normals, texture coordinates and their connectivities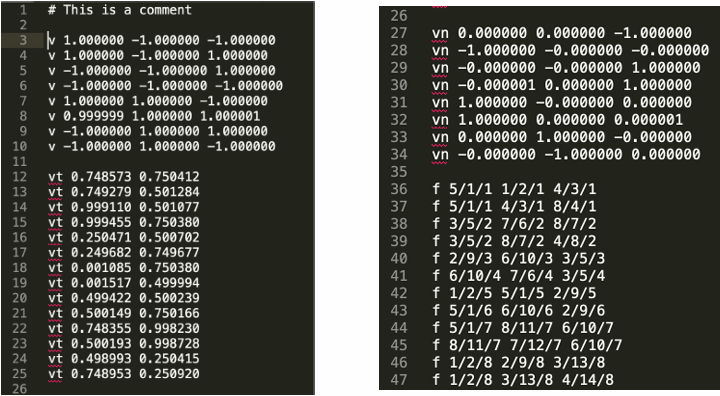
v 顶点坐标 vt 纹理坐标 vn 法线方向
f 三角形顶点选择 5/1/1 —> v/vt/vn
Curves
Bézier Curves
Consider three points (quadratic Bezier) – de Casteljau Algorithm
定义起点在时间0,终点在时间1,在b0、b1间取得t时刻的点b01
类比在b1和b2间也取得t时刻的点b11,最后在b01和b11间取得t时刻的点b02
最后Run the same algorithm for every t in [0,1]
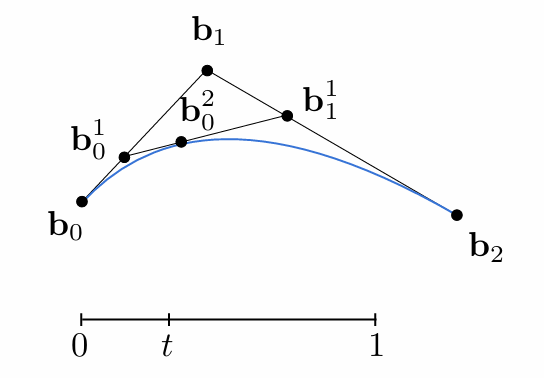
Four input points in total
Same recursive linear interpolations
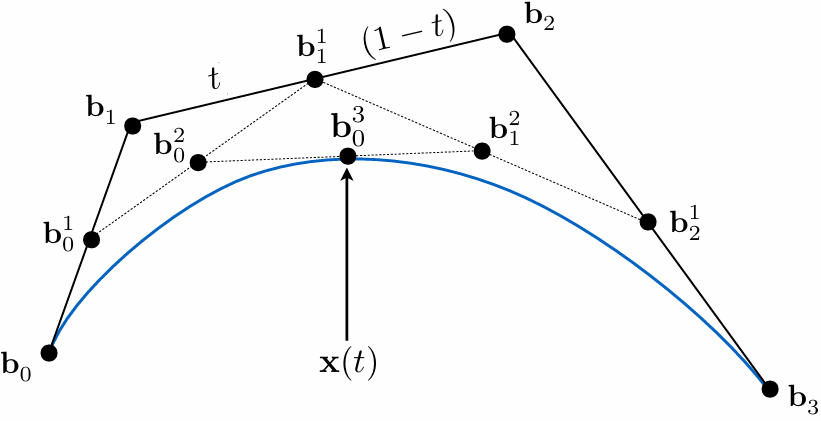
Bézier Curve – General Algebraic Formula
Bernstein form of a Bézier curve of order n:
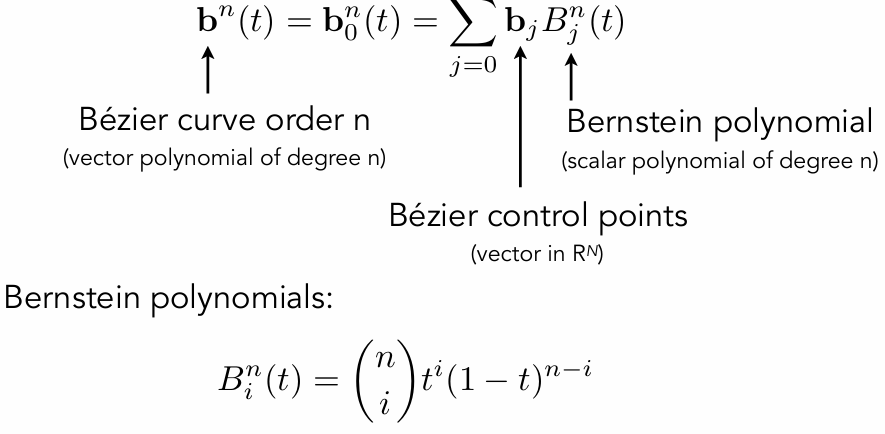
伯恩斯坦多项式:i –> 0~n 的求和为1 括号(n i)表达的是C(i n),组合的结果
Properties of Bézier Curves
Interpolates endpoints
• For cubic Bézier:
b(0) = b0; b(1) = b3
Tangent to end segments 相切
• Cubic case:
b0(0) = 3(b1 b0); b0(1) = 3(b3 b2)
Affine transformation property
• Transform curve by transforming control points
Convex hull property
• Curve is within convex hull of control points
Piecewise Bézier Curves 逐段贝塞尔曲线
高阶贝塞尔曲线很难控制,不够直观
Instead, chain many low-order Bézier curve
Piecewise cubic Bézier the most common technique
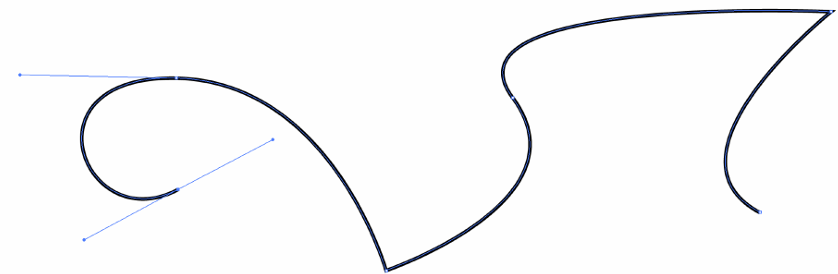
Widely used (fonts, paths, Illustrator, Keynote, …)
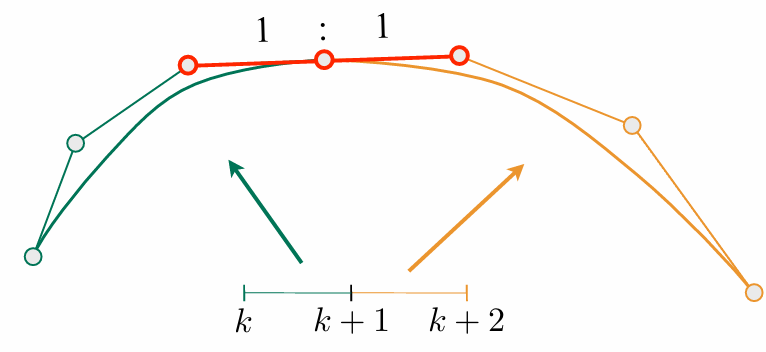
Piecewise Bézier Curve – Continuity
C0连续
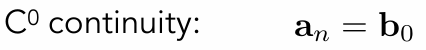
C1连续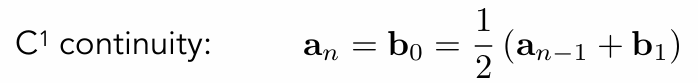
Other types of splines 样条
• Spline
A continuous curve constructed so as to pass through a given set of points and have a certain number of continuous derivatives.
In short, a curve under control
• B-splines 相比贝塞尔曲线具有局部性(一个控制点的变化只会影响局部曲线)
-Short for basis splines
-Require more information than Bezier curves
-Satisfy all important properties that Bézier curves have (i.e. superset)
Surfaces
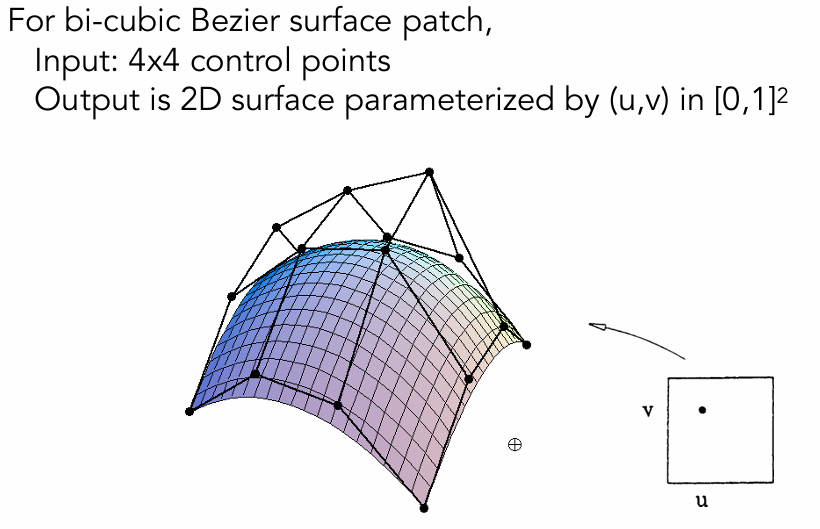
Bézier Surfaces
Extend Bézier curves to surfaces
Bicubic Bézier Surface Patch
Evaluating Surface Position For Parameters (u,v)
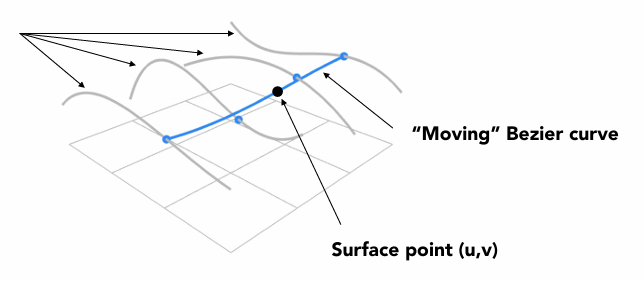
Method: Separable 1D de Casteljau Algorithm
Goal: Evaluate surface position corresponding to (u,v)
(u,v)-separable application of de Casteljau algorithm
• Use de Casteljau to evaluate point u on each of the 4 Bezier curves in u. This gives 4 control points for the “moving” Bezier curve
• Use 1D de Casteljau to evaluate point v on the “moving” curve
Mesh Operations: Geometry Processing
• Mesh subdivision
• Mesh simplification
• Mesh regularization