Application of textures 贴图的应用
In modern GPUs, texture = memory + range query (filtering)
• General method to bring data to fragment calculations
Many applications
• Environment lighting
• Store microgeometry
• Procedural textures
• Solid modeling
• Volume rendering
Environment Map 环境贴图

Spherical Map
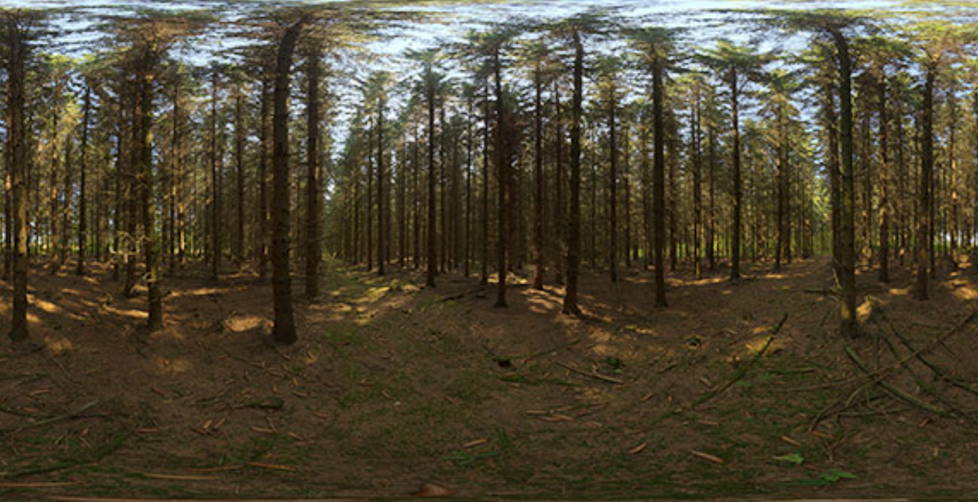

问题:Prone to distortion (top and bottom parts)!
Cube Map
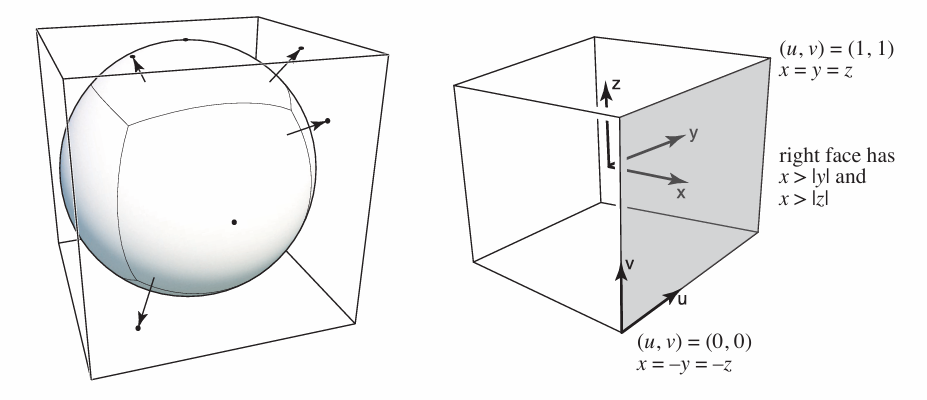
A vector maps to cube point along that direction.
The cube is textured with 6 square texture maps.
Much less distortion!
Need dir->face computation
Textures can affect shading
Textures doesn’t have to only represent colors
-What if it stores the height / normal?
-Bump / normal mapping
-Fake the detailed geometry
Bump Mapping 凹凸贴图
Adding surface detail without adding more triangles
•Perturb surface normal per pixel (for shading computations only)
•”Height shift” per texel defined by a texture
•How to modify normal vector?
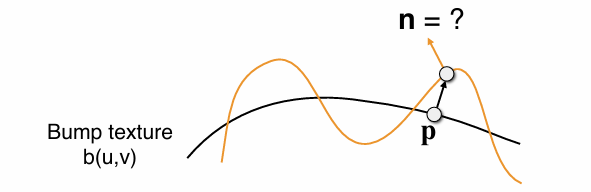
Perturb the normal(in flatland)计算法线的扰动
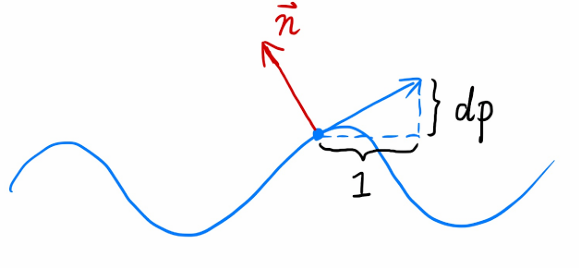
• Original surface normal n(p) = (0, 1)
• Derivative at p is dp = c * [h(p+1) - h(p)] 计算斜率向量(1,dp)
• Perturbed normal is then n(p) = (-dp, 1).normalized() 逆时针旋转90度得到法线向量(-dp,1)
Perturb the normal(in 3D)
• Original surface normal n(p) = (0, 0, 1)
• Derivatives at p are - dp/du = c1 * [h(u+1) - h(u)] - dp/dv = c2 * [h(v+1) - h(v)]
• Perturbed normal is n = (-dp/du, -dp/dv, 1).normalized()
Note that this is in local coordinate (认为局部地方的法线为(0,0,1))
Displacement mapping 位移贴图- a more advanced approach
使用和凹凸贴图相同的贴图
Actually moves the vertices
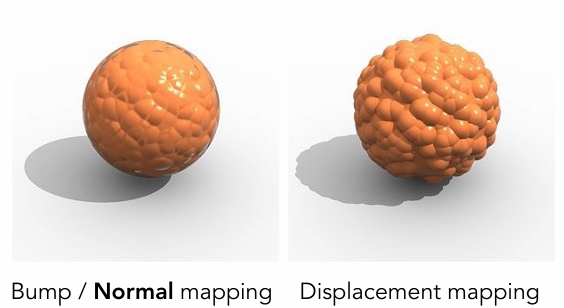
需要模型的三角形足够细致
3D Procedural Noise + Solid Modeling
利用三维噪声来生成外表
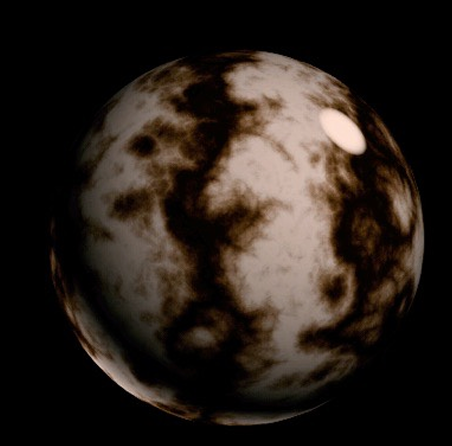
(Perlin noise, Ken Perlin)
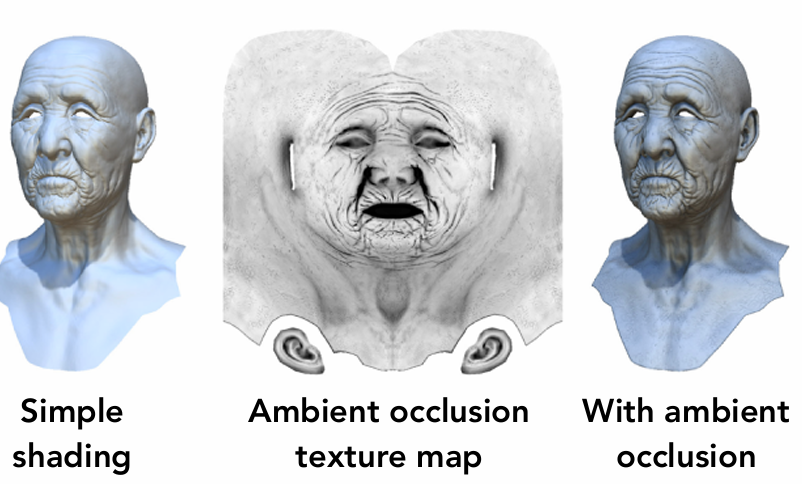
Provide Precomputed Shading
3D Textures and Volume Rendering
Introduction to geometry
Examples of geometry
各种几何图形
Various representations of geometry
Implicit
• algebraic surface
• level sets
• distance functions
• …
Explicit
• point cloud
• polygon mesh
• subdivision, NURBS
• …
Each choice best suited to a different task/type of geometry
Implicit Representation of Geometry
Based on classifying points
• Points satisfy some specified relationship
E.g. sphere: all points in 3D, where x^2+y^2+z2 = 1
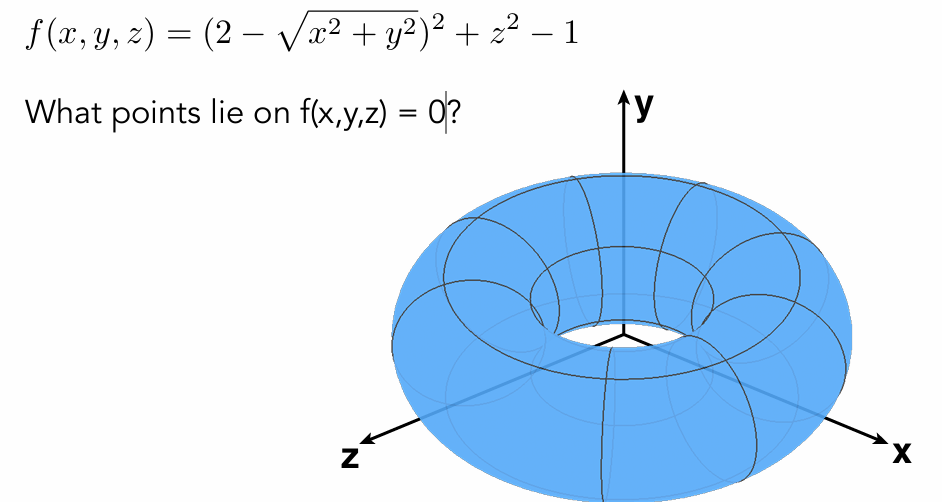
More generally, f(x,y,z) = 0
容易用于判断点在范围内外,但是很难直接得到面上所有的点。
Implicit surface
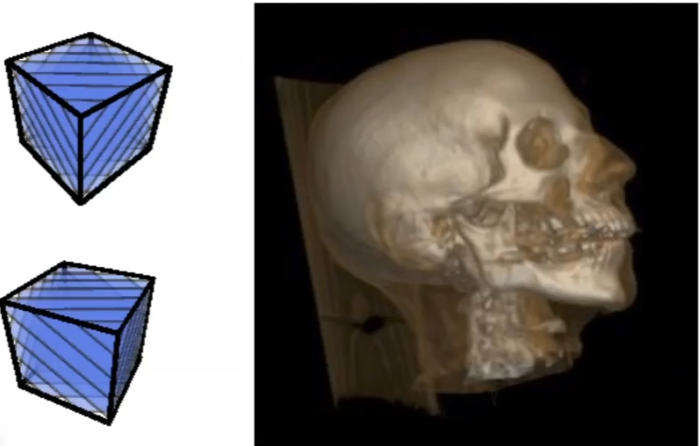
Sampling Can Be Hard
Explicit Representation of Geometry
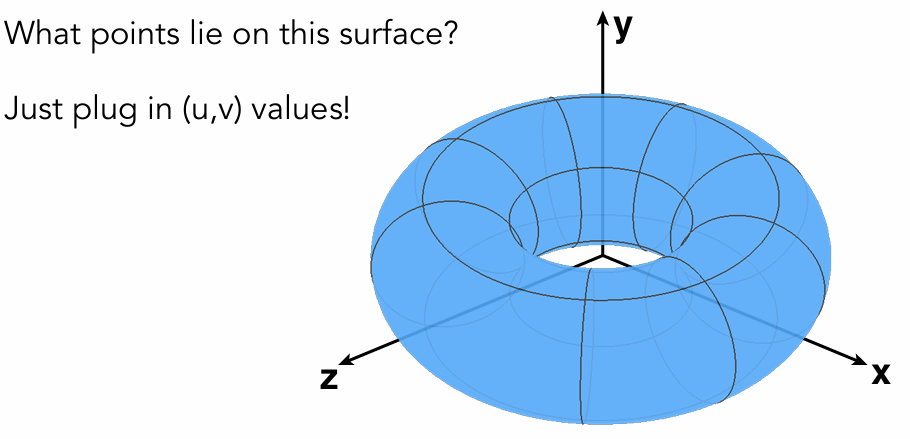
f(u,v) = ((2 +cosu)cosv,(2+cosu)sinv,sinu)
Explicit surface
Sampling is easy!但是很难判断一个点在表面内外
Many Implicit Representations in Graphics
Algebraic Surfaces (Implicit)
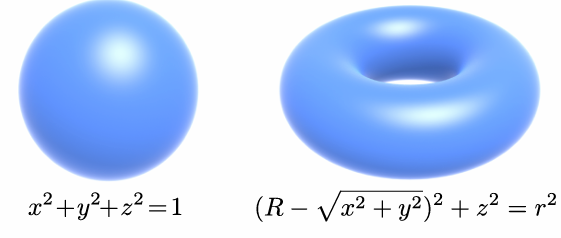
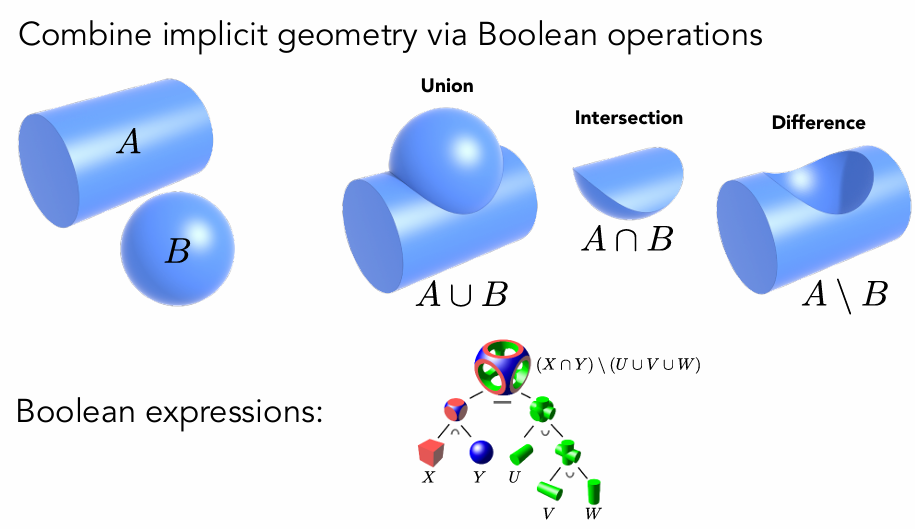
Constructive Solid Geometry (Implicit)
Combine implicit geometry via Boolean operations
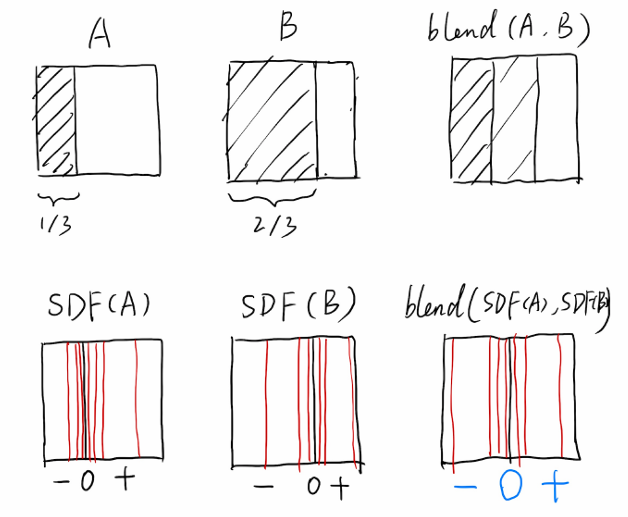
Distance Functions (Implicit)
Instead of Booleans, gradually blend surfaces together using
Distance functions:
giving minimum distance (could be signed distance) from anywhere to object
An Example: Blending (linear interp.) a moving boundary
SDF = signed distance function
Level Set Methods (Also implicit)
Closed-form equations are hard to describe complex shapes
Alternative: store a grid of values approximating function
Surface is found where interpolated values equal zero 用插值求到所需的表面
Provides much more explicit control over shape (like a texture)
Fractals (Implicit)
Exhibit self-similarity, detail at all scales
“language” for describing natural phenomena
Hard to control shape!
Implicit Representations - Pros & Cons
Pros:
• compact description (e.g., a function)
• certain queries easy (inside object, distance to surface)
• good for ray-to-surface intersection (more later)
• for simple shapes, exact description / no sampling error
• easy to handle changes in topology (e.g., fluid)
Cons:
• difficult to model complex shapes