3D transformation
1.3D homogeneous coordinates:
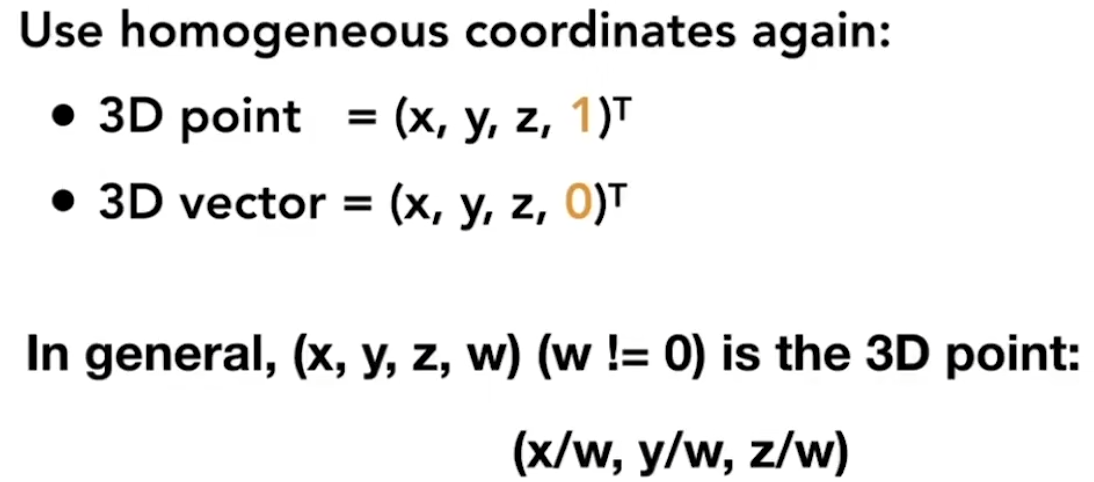
2.3D affine transformations:
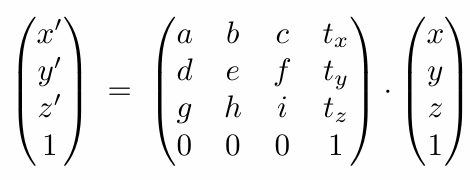
问题:对于仿射变换而言,是先进行平移还是线性变换?
展开后可以得到,是先应用的线性变换,再加上的平移量
3.Rotation around x y z -axis
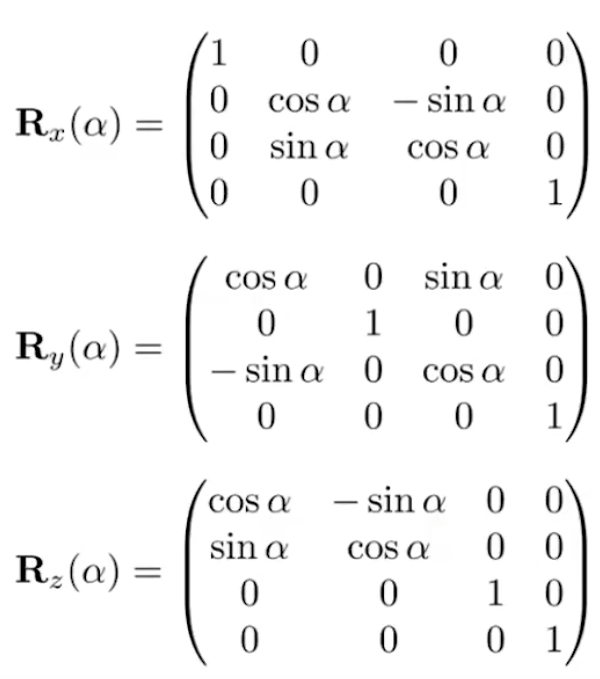
为什么R_y的sin的符号不一样?
因为应该按照右手螺旋定则 应该是zx -》+ y,所以xz是相反的-y
4.Rodrigues’ Rotation Formula
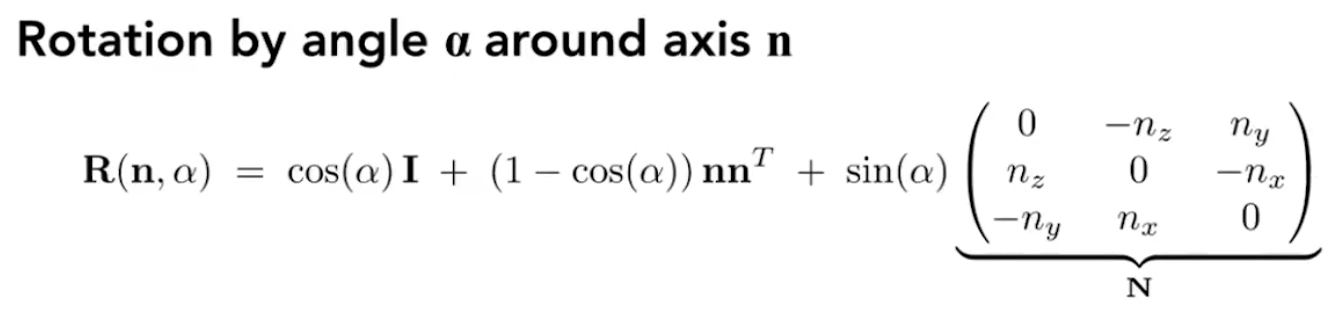
View/Camera Transformation
定义一个相机:
- 位置
- 视线方向
- 向上方向
关键点:当相机和物体一起移动,相片不变
约定:
1.移动相机到The origin, up at Y, look at -Z
2.同时让物体进行相同的移动
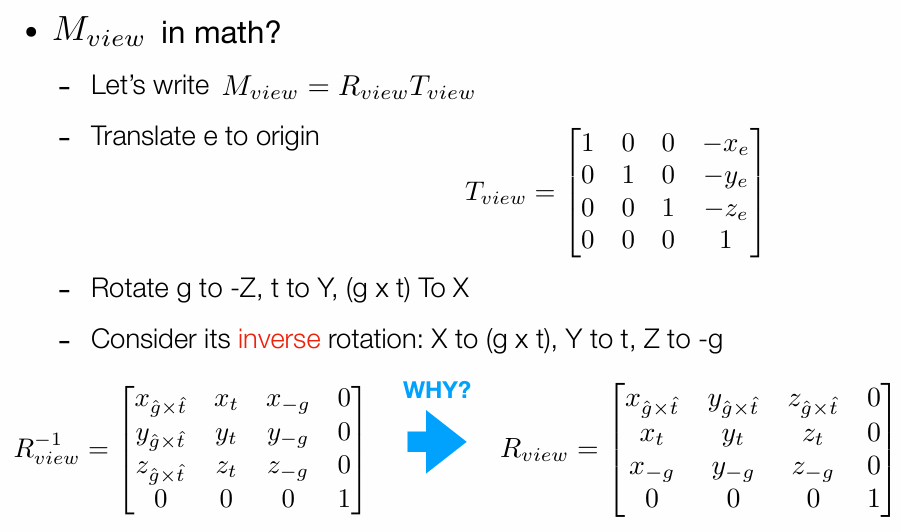
因为要先平移再旋转,所以不能直接用仿射变换写出来,要两个单独写再相乘。
Projection transfomsation
Orthographic projection
Translate (center to origin) first, then scale (length/width/height to 2)
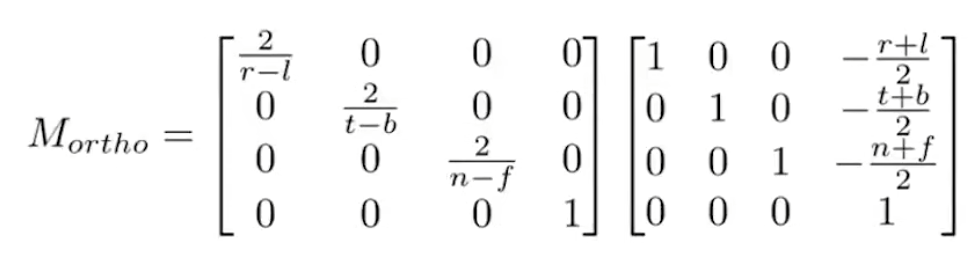
摄像头沿着-z看,所以n>f。
所以OpenGL使用了左手坐标系,来让n<f。
Perspective projection
先从透视到正交 M_persp->ortho,再做正交投影 M_ortho
推导 M_persp->ortho:想象将furstum挤压为cuboid
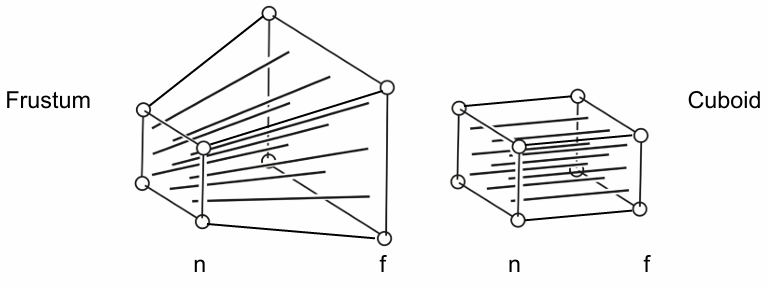
约定:near面和far面都不变,即z不会变化。并且中心点不会发生变化。先用所有同一个面的x, y和near plane满足相似关系,推导出x,y的变换。
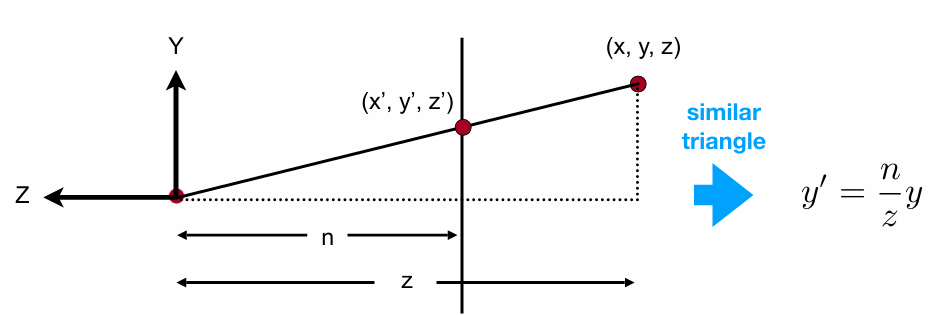
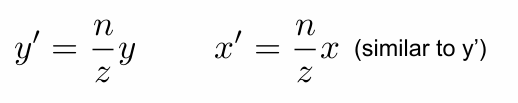
得到变换前后关系:(广义坐标homogeneous coordinates)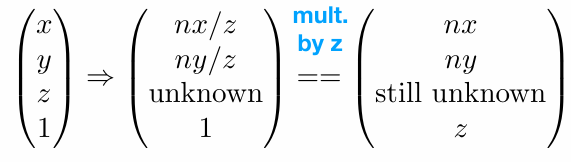
由此推导出变换矩阵的大部分参数: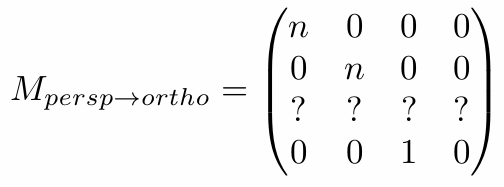
再用near plane需要所有点不变以及far plane的z坐标不变(特别是far plane的中心点完全不变),推导出z的变换。
Any point on the near plane will not change
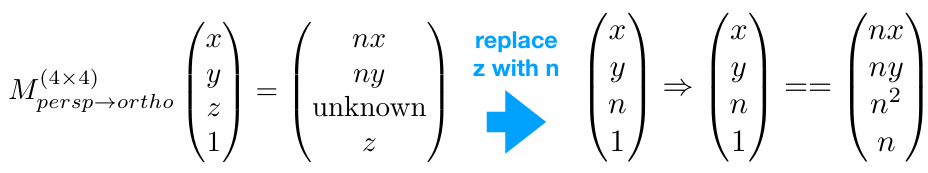
So the third row must be of the form (0 0 A B)
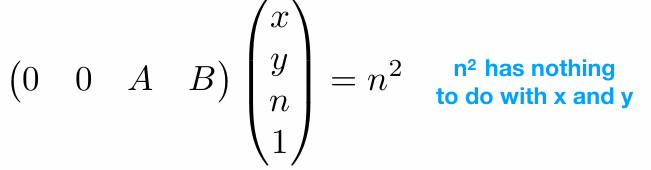
Any point’s z on the far plane will not change
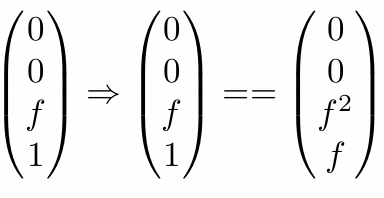
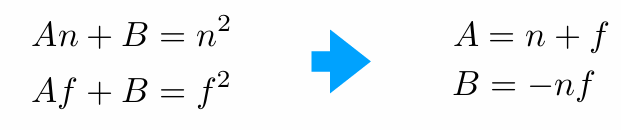
两个方程,两个未知数,可解出A和B的值:
透视投影矩阵 = 正交投影矩阵 * 透视到正交矩阵